Features
There are a lot of well known projects, and hidden gems, which aid in your productivity; this project aims to install the best of them to make life a little easier.
- For everybody
- For command line users
- For GUI desktop users
- For developers
- For containerized development
- For Java developers
- For Node.js developers
- For Python developers
- For Ansible developers
For everybody
Dynamically allocated swap space
Website: https://github.com/Tookmund/Swapspace
Swapspace is a dynamic swap manager for Linux. It dynamically allocates file based swap space to provide virtual memory when needed.
Compressed swap
Website: https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/vm/zswap.txt
Zswap is a kernel feature that provides a compressed RAM cache for swap pages.
Unless you have 16GB of RAM you’re probably going to struggle to run VirtualBox, your IDE, a Maven build, your application, and a few services in Docker at the same time.
Enabling swap compression in the virtual machine allows you to run more things at once before swap I/O performance becomes an issue.
File backup & restore between rebuilds
Website: https://rsync.samba.org
One of the advantages of using a virtual machine is it’s easy to get back to a clean working state by rebuilding the virtual machine.
However, you want to keep your user-specific setup, and your workspace with all the repositories you’ve cloned.
This project uses rsync to backup selected files and folders from the client virtual machine to a separate persistent virtual disk on the host machine.
When the virtual machine is rebuilt, these files and folders are copied back to the new client virtual machine.
The following are some of the files and folders backed-up by default:
-
/home/dev/workspace/- Put all your projects here
/home/dev/.gitconfig/home/dev/.ssh/(except theauthorized_keysfile)/home/dev/.gnupg//home/dev/.m2/(except therepositoryandwrapperdirectories)
Caution: the followings directories are excluded from the backup by
default: .bin, .molecule, .tmp, bin, build, node_modules, target.
Note: you can find your backup under: /var/persistent/home/dev/.
Notice: we accept no responsibility for files lost due to a failure of the backup/restore process. We recommend you push your work to your source control server before rebuilding your virtual machine. We also recommend you manually backup important keys and certificates (e.g. SSH, GPG, X.509) on your host machine.
For command line users
Terminator
Website: http://gnometerminator.blogspot.co.uk/p/introduction.html
A highly customizable terminal emulator that supports splitting the screen into grids of separate console windows (as well as supporting multiple tabs).
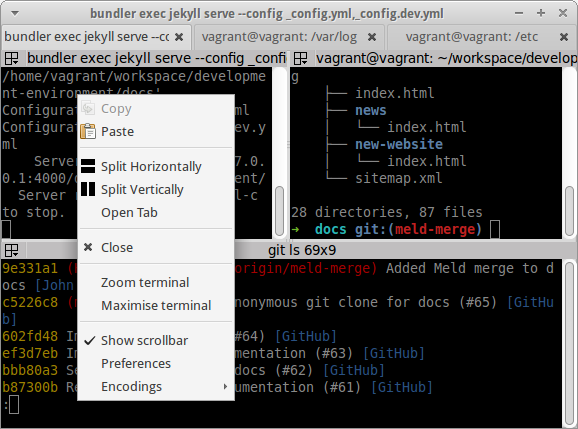
Tip: right click on the window to bring up the menu to split the screen or open a new tab.
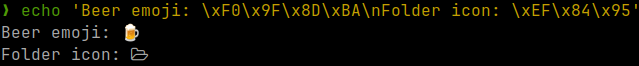
Fonts
NotoColorEmoji: https://github.com/googlefonts/noto-emoji
JetBrainsMono Nerd Font: https://www.nerdfonts.com
Many modern command line tools output emojis so we’ve included NotoColorEmoji to display those characters. Starship prompt and LSD also require a Nerd Font to display correctly, so we’ve included JetBrainsMono Nerd Font.
CDPATH
Website: http://zsh.sourceforge.net/Intro/intro_13.html
This environment variable changes how tab completion and the cd command works.
We’ve added the /home/dev/workspace directory to CDPATH; this enables
you to cd into any sub-directory of /home/dev/workspace from any
directory in the file system.
For example:
# Create a directory under /home/dev/workspace
mkdir -p /home/dev/workspace/my-awesome-project
# Change directory somewhere else
cd /etc
# Use tab completion (from /etc)
cd my-awe<TAB>
# Change directory to my-awesome-project (from /etc)
cd my-awesome-project
# Check you're in the right directory
pwd
/home/dev/workspace/my-awesome-project
This makes it really quick and easy to access your project directories.
Oh My Zsh
Website: http://ohmyz.sh
Rather than a specific command, Oh My Zsh changes your default shell from bash
to zsh, and customizes the zsh shell.
Oh My Zsh gives you:
- Better tab completion (like expanding partial names in path).
- Themes to enhance your command prompt (like showing the current git branch).
- Plugins to enable command specific tab completion (e.g.
mvnandgit).
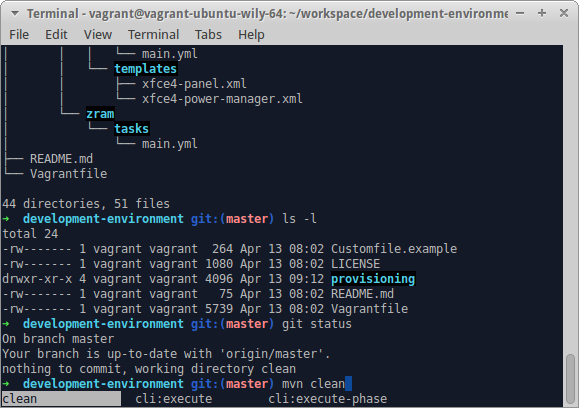
Try this:
cat /u/s/a/vim<TAB>
# Expands to:
cat /usr/share/applications/vim.desktop
Tip: tab-completion for command options often only works after you’ve specified
the -. For example grep TAB produces no suggestions, but grep - TAB
produces 160 suggestions.
Zim
Website: https://zimfw.sh
Oh My Zsh has a wide selection of plugins, but sometimes you want to install plugins from elsewhere. This is where Zim comes in, Zim is a plugin manager for Zsh and can install Zsh plugins from Git repositories.
You can find a list of third-party plugins at: https://github.com/unixorn/awesome-zsh-plugins/blob/main/README.md
Starship Prompt
Website: https://starship.rs
A fast command line prompt with lots of features.
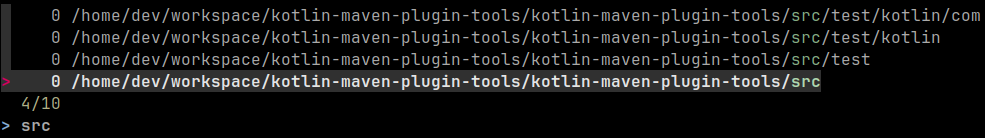
Zoxide
Website: https://github.com/ajeetdsouza/zoxide
Easily cd into directories you’ve previously visited. Run zi so see a
searchable list of previous directories.
Generic Colouriser
Website: https://github.com/garabik/grc
Colorizes the output of several common command line tools.
fzf
Website: https://github.com/junegunn/fzf
Command line fuzzy finder.
Integrates in several ways:
- Reverse shell history search
CTRL-R - Find files or directories e.g.
cd **<TAB> - Complete process IDs e.g.
kill -9 **<TAB>
fzf-tab is used to integrate fzf with
Zsh tab completion.
LSD (LSDeluxe)
Website: https://github.com/lsd-rs/lsd
A ls replacement with more colorful output filetype icons. A Zsh alias is used
to invoke lsd when running ls.
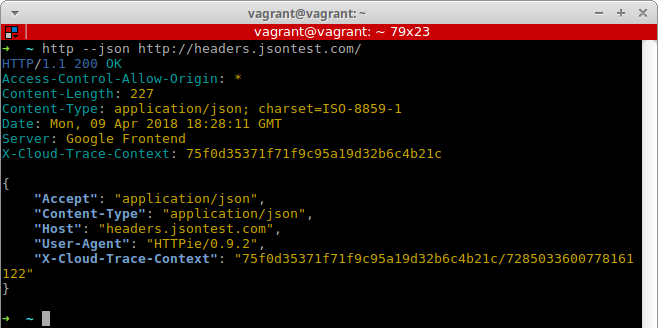
HTTPie
Website: https://httpie.org
HTTPie is a command line HTTP client. HTTPie is somewhat like cURL or Wget, but designed more for interactive use than use in shell scripting. It has a more intuitive command line interface, JSON support and syntax highlighting.
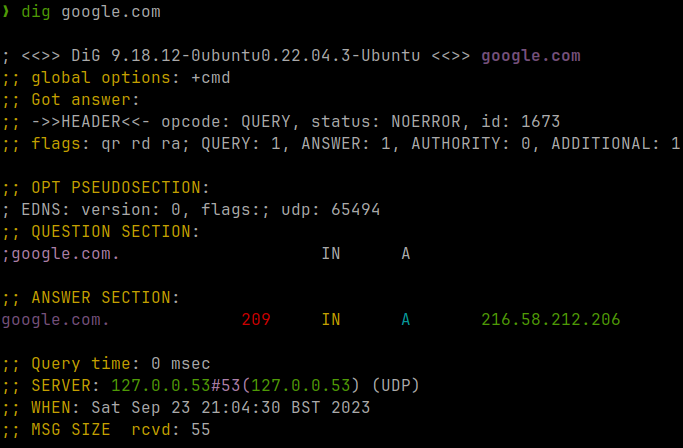
The Silver Searcher
Website: http://geoff.greer.fm/ag
If you’ve used Linux you’ve almost certainly used grep, but you’ve probably
never heard of ag (The Silver Searcher).
While grep is a great general purpose tool, ag is a specific tool for
finding matching text in a directory tree and outputting the results in a human
readable format.
Below is the output of the command ag java on this project:
Tip: if you have multiple pages of output you may want to use
ag --pager=less PATTERN.
Tree
Website: http://mama.indstate.edu/users/ice/tree
The tree command is similar to find . but outputs in a graphical tree
format.
Below is the output of the command tree on this project:
Tip: if you have multiple pages of output you may want to use
tree -C | less -R.
Jq
Website: https://stedolan.github.io/jq
The jq command would be worth installing just to be able to use it to pretty
print JSON in colour, but jq is amazing at manipulating JSON as well.
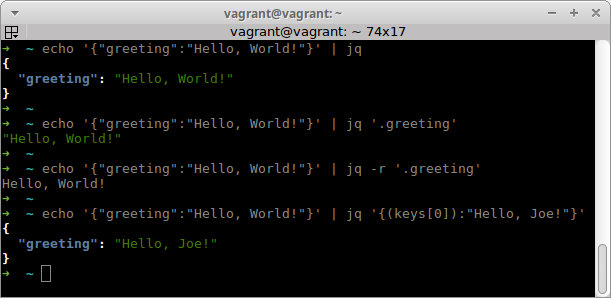
Tip: to pretty print a JSON file run jq '.' PATH_TO_JSON_FILE.
fd
Website: https://github.com/sharkdp/fd
fd is a simple, fast and user-friendly alternative to find.
It’s much better for the most common use-case (i.e. finding files/directories by name) e.g:
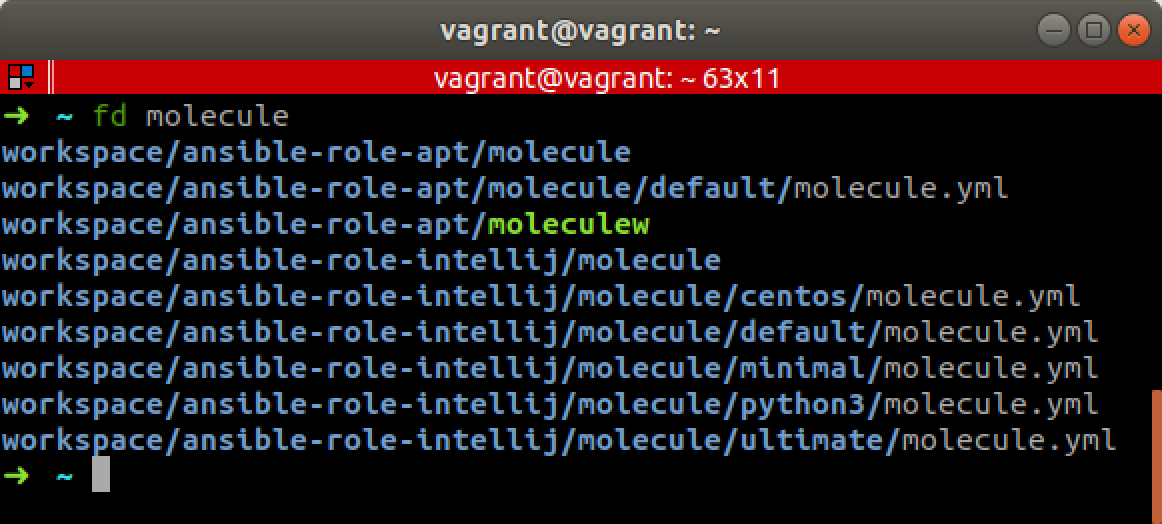
This is obviously easier than find -iname '*molecule*'.
fd is still capable of handling more advanced use-cases as well, e.g. you can
specify the type of file or a command to execute.
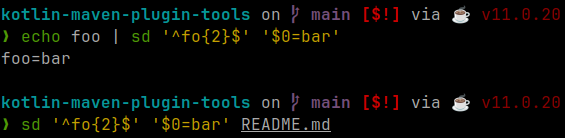
sd
Website: https://github.com/chmln/sd
A tool for performing find and replace in files/streams from the command line.
Simple alternative to sed.
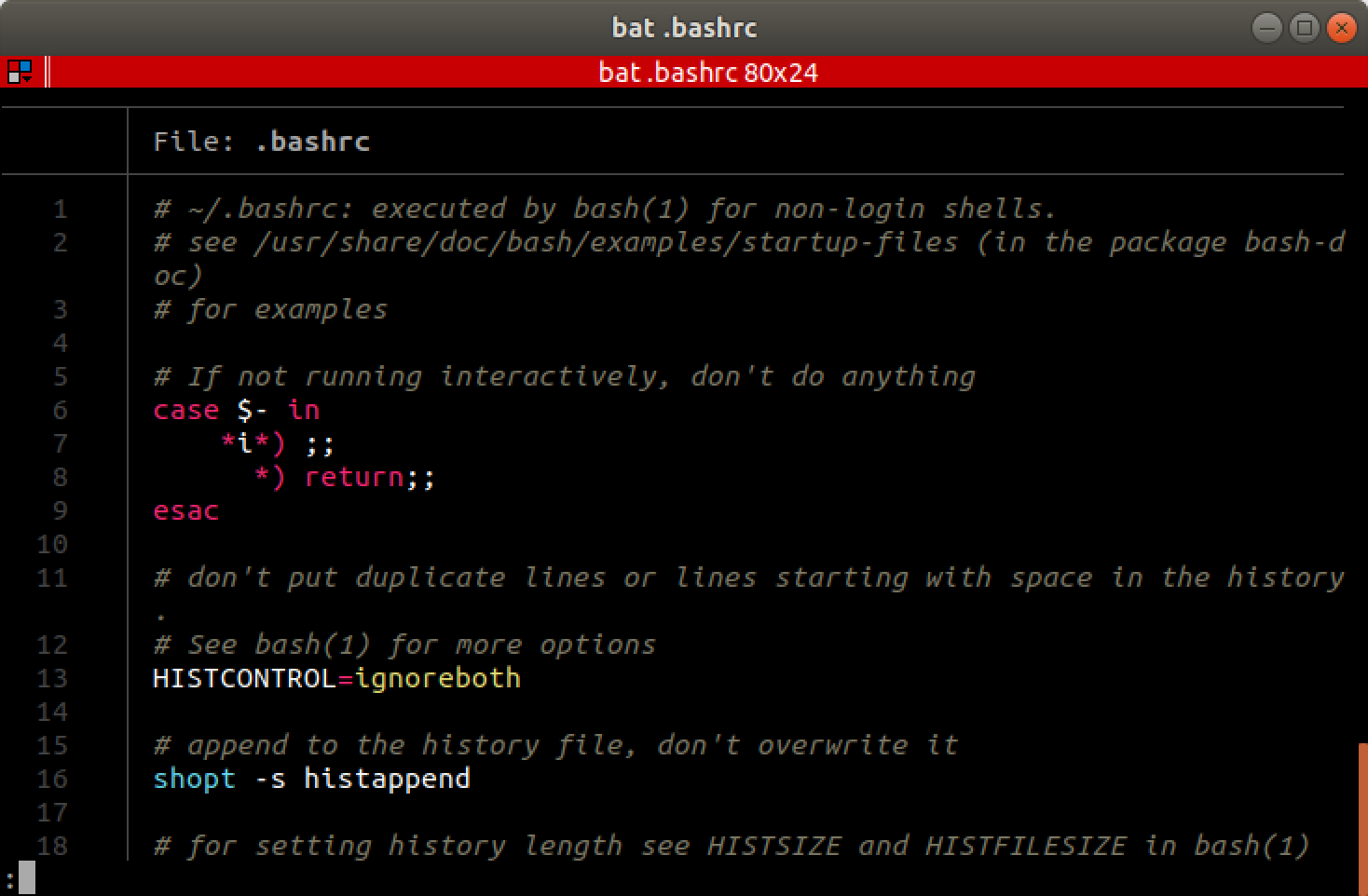
bat
Website: https://github.com/sharkdp/bat
bat is a more advanced alternative to cat with support for
syntax-highlighting, line numbers, searching and paging.
e.g. running bat ~/.bashrc will give you:
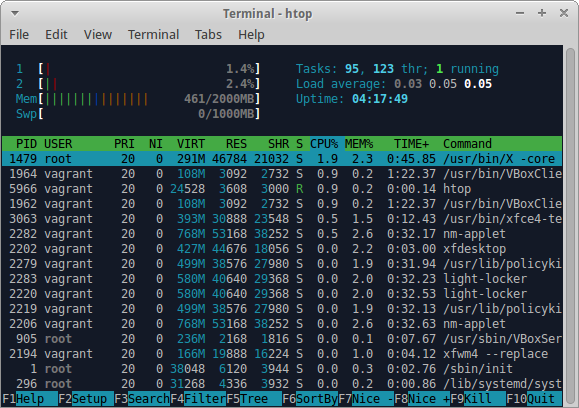
htop
Website: http://hisham.hm/htop
The htop command is essentially a top replacement with a better looking user
interface and a few more features.
Glances
Website: https://nicolargo.github.io/glances
The glances application shows a broader view of what’s going on on your system
than top or htop provide. In addition to RAM and CPU usage, you can see
disk I/O, network I/O and warnings/alerts.
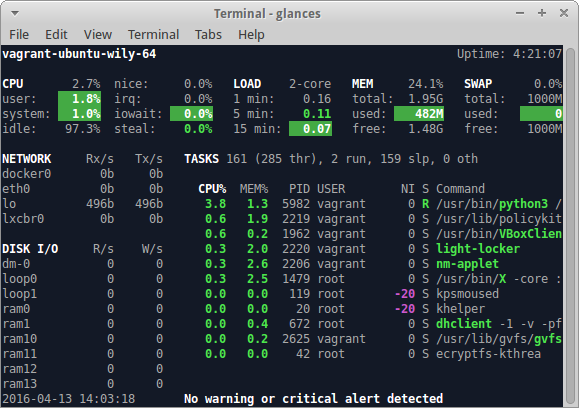
Btop++
Website: https://github.com/aristocratos/btop
Btop++ shows a broad view of the what’s going on on your system in a more
graphical style.
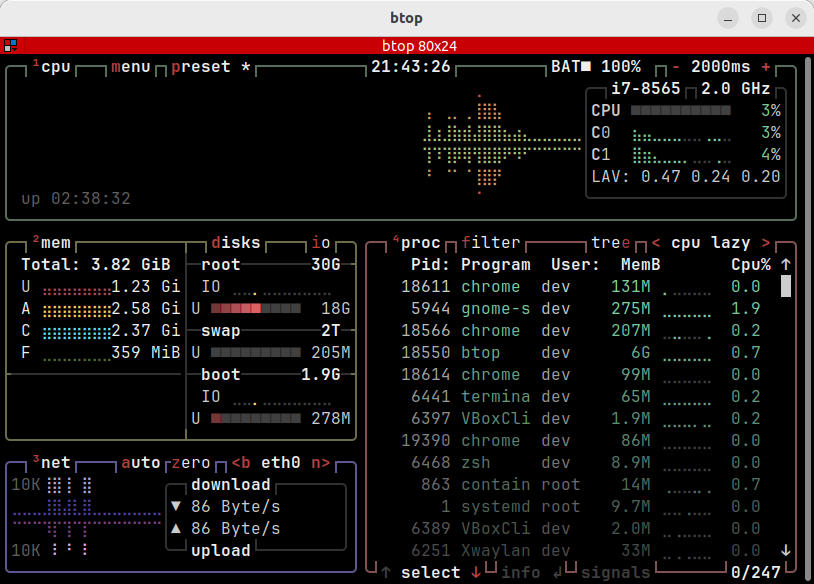
lnav
Website: https://lnav.org
A tool for viewing and navigating log files.
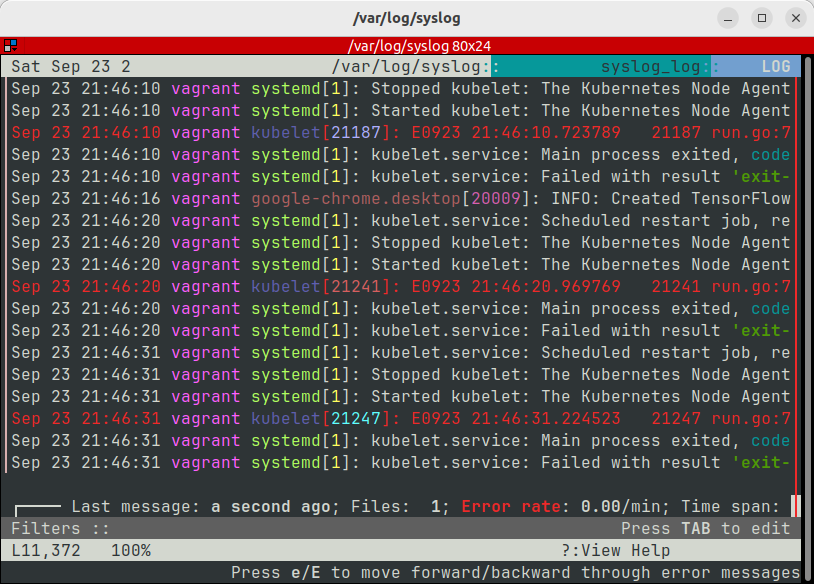
duf
Website: https://github.com/muesli/duf
An alternative to df for showing disk usage and free space.
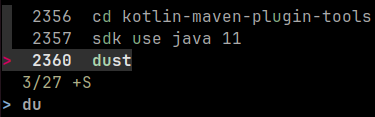
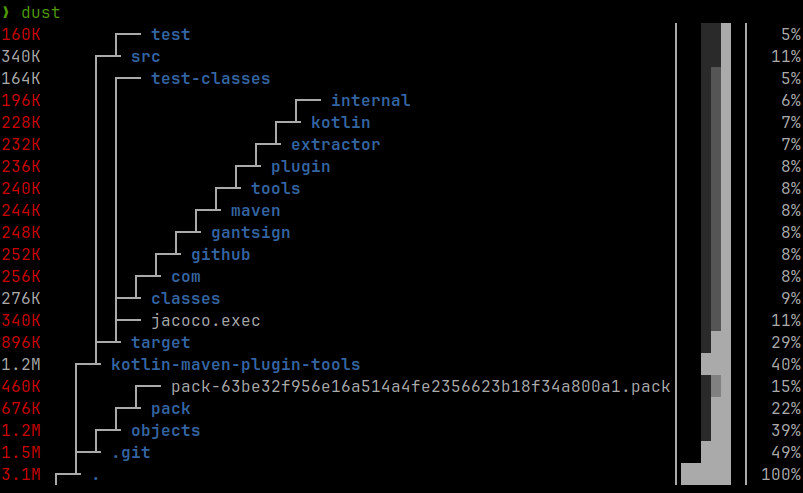
dust
Website: https://github.com/bootandy/dust
A more graphical alternative to du for displaying dusk usage for files and
directories.
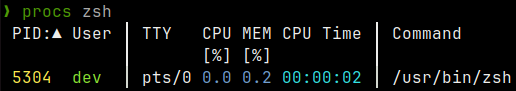
procs
Website: https://github.com/dalance/procs
An improved alternative to ps with color output and additional features.
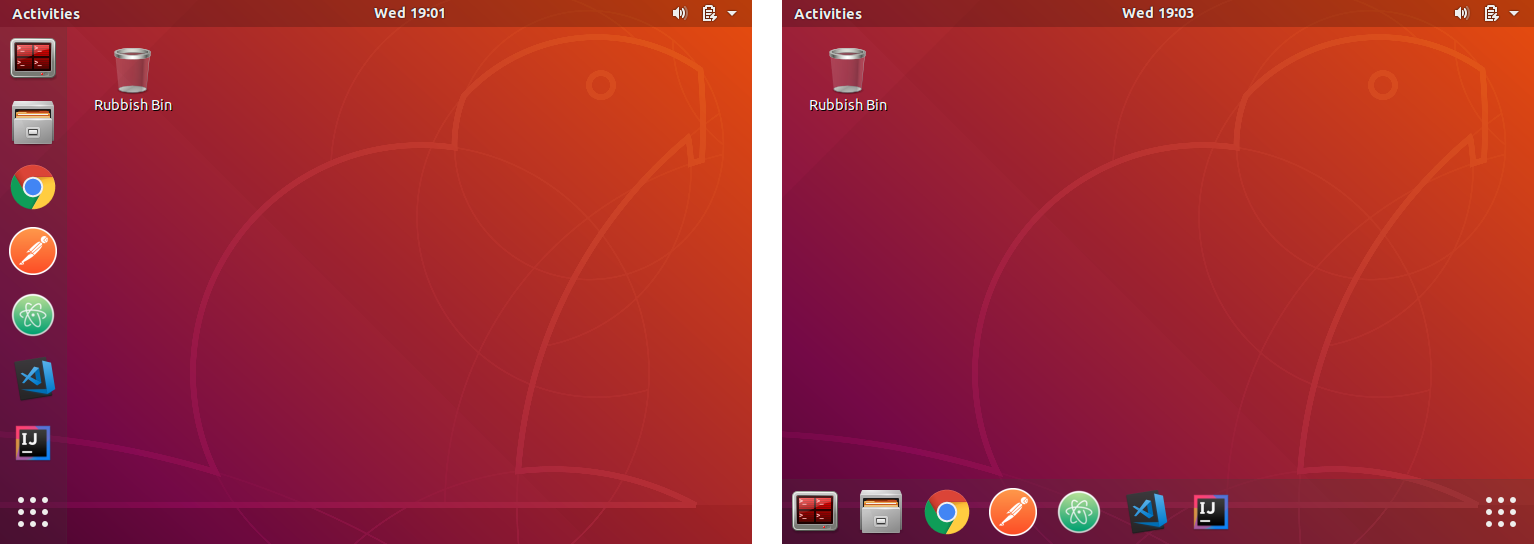
For GUI desktop users
Pre-pinned applications
No more fishing through menus to run the applications you use the most. The provisioning script pre-pins selected applications to the dock so they’re ready to use.

Choice of dock position
Each user can choose whether they want the dock bar on the left, right or bottom of the screen.
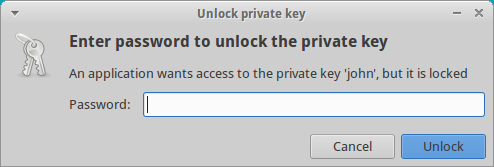
Seahorse
Website: https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Seahorse
Graphical user interface for managing your keys, and a SSH agent to save you having to put in your SSH password more than once in the same session.
For developers
IntelliJ IDEA IDE
Website: https://www.jetbrains.com/idea
In my opinion IntelliJ IDEA is the best IDE whether you’re working in Java, Python or Node.js (Node.js support requires IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate Edition).
The Community Edition is excellent at what it does but it’s quite limited in support for languages and frameworks. You need to pay for the Ultimate Edition if you want support for common tools/frameworks such as JavaEE and the Spring Framework. The relatively small price for the Ultimate Edition is well worth the money.
By default the Community Edition is installed.
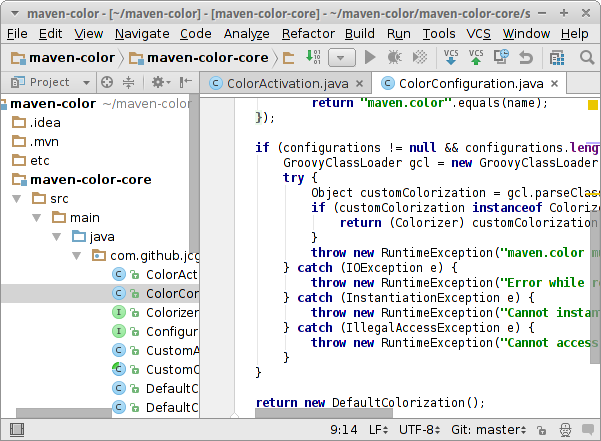
IntelliJ plugins
- Indent Rainbow add color to the indent based on the indent level.
- Rainbow Brackets add color to brackets based on nested pairs.
- String Manipulation case switching, sorting, filtering etc.
- Save Actions - XDEV Edition re-format/clean-up code on save.
-
PlantUML integration for drawing diagrams using the PlantUML domain-specific language.
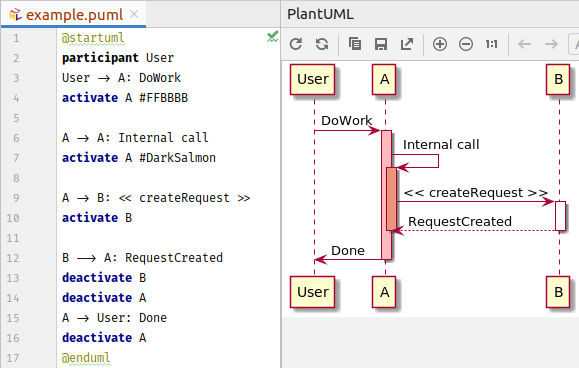
Visual Studio Code
Website: https://code.visualstudio.com
Great support for YAML, Markdown, HTML, CSS, LESS, SASS, JavaScript, TypeScript, Node.js, Python, Bash and many more.
Core languages have IntelliSense support for smart completion.
The built in debugger is very good and supports several languages.
Has good built-in support for Git; while, it’s missing a few features that you’d expect from a standalone Git client, it covers the normal development workflow.
Tip: click on the branch name in the bottom left corner to change/create branches.
EditorConfig
Website: http://editorconfig.org
EditorConfig is a project that defines a common configuration file supported by many IDEs and text editors (some require a plugin installed).
The EditorConfig configuration file defines the basic editor preferences for particular files and file types (e.g. charset, line endings, indent, trailing whitespace).
This development environment installs the EditorConfig plugin for Visual Studio Code as part of the provisioning; IntelliJ IDEA supports EditorConfig without the need for a plugin.
For an example of an .editorconfig file see the root directory of this
project.
Git aliases
Git aliases save you a lot of typing and make it easy to execute more complex Git commands:
-
Print the main branch (searches for
main,trunk,mainline,defaultandmaster)git main=git-main-branch(shell script) -
Print the develop branch (searches for
dev,devel,developmentanddevelop)git dev=git-develop-branch(shell script) -
Print the remote
HEADbranchgit rhead=git remote show origin | grep -Po 'HEAD branch: \K.*' -
Print the repository root directory
git root=git rev-parse --show-toplevel -
Execute a command in the repository root
git exec=f() { exec "$@"; }; f(shell function) -
View summary lines for recent commits
git ls≡git log --pretty=format:"%C(yellow)%h%Cred%d\ %Creset%s%Cblue\ [%an]" --decorate -
View summary lines and list changed files for recent commits
git ll≡git log --pretty=format:"%C(yellow)%h%Cred%d\ %Creset%s%Cblue\ [%an]" --decorate --numstat -
View summary lines and dates for recent commits
git lds≡git log --pretty=format:"%C(yellow)%h\ %ad%Cred%d\ %Creset%s%Cblue\ [%an]" --decorate --date=short -
View tree of recent commits (all branches)
git lt≡git log --oneline --graph --decorate --all -
Switch to an existing branch
git sw≡git switch -
Create a new branch
git cb≡git switch -c -
Amend the last commit and change the commit message
git ca≡git commit --amend -
Amend the last commit without changing the commit message
git cane≡git commit --amend --no-edit -
Rebase the current branch onto
origin/maingit rom≡git fetch -p && git rebase origin/$(git main) -
Rebase the current branch onto
origin/developgit rod≡git fetch -p && git rebase origin/$(git dev) -
Rebase the current branch onto
origin/HEADgit roh≡!git fetch -p && git rebase origin/$(git rhead) -
Push the current branch to
origin HEADgit po≡git push origin HEAD -
Force push the current branch to
origin HEADgit pof≡git push origin HEAD --force -
Switch to the
mainbranch, pull changes and prune remote branchesgit smp≡git switch $(git main) && git pull -p -
Switch to the
developbranch, pull changes and prune remote branchesgit sdp≡git switch $(git dev) && git pull -p -
Switch to the local branch with the same name as the remote head, pull changes and prune remote branches
git shp≡git fetch -p && git switch $(git rhead) && git pull -p -
Pop the most recent stash
git pop≡git stash pop -
List the most recently checked-out branches
git lb≡git reflog show --pretty=format:'%gs ~ %gd' --date=relative | grep 'checkout:' | grep -oE '[^ ]+ ~ .*' | awk -F~ '!seen[$1]++' | head -n 10 | awk -F' ~ HEAD@{' '{printf(" \033[33m%s: \033[37m %s\033[0m\n", substr($2, 1, length($2)-1), $1)}' -
Reformat the recent changes as Markdown release notes
git release-notes≡git log --color --pretty=format:'%s%Cred%d%Creset' --decorate | sed -E 's/(.*) \((\#[0-9]+)\)/* \2: \1/' | tac -
Git-GUI
Website: https://git-scm.com/docs/git-gui
Git-GUI and Gitk (see below) are companion applications that together make the most fully featured open source GUI Git client available for Linux.
Git-GUI is the commit dialog and the UI for performing remote operations.
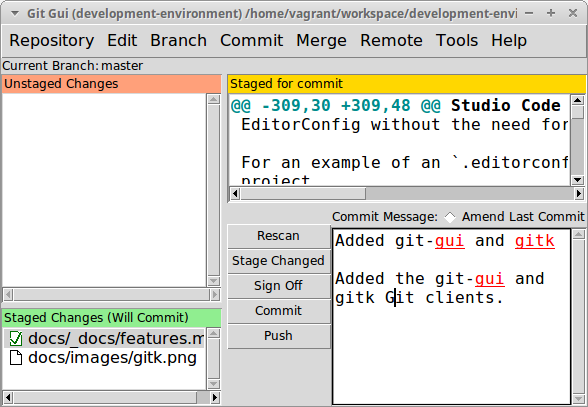
Generally, I’d advise only using Git-GUI when you need to amend a commit, the rest of the time you’re better off using the commit dialog in your editor/IDE.
Tip: run git gui in your Git working directory to launch Git-GUI.
Gitk
Website: https://git-scm.com/docs/gitk
Gitk and Git-GUI (see above) are companion applications that together make the most fully featured open source GUI Git client available for Linux.
Gitk is the repository/history browser.
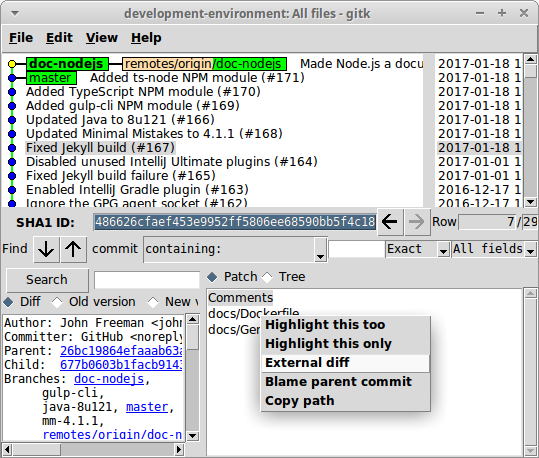
As you can see it’s not the prettiest application, but the other options are either not free for commercial use, require registration to download, or lack support for resetting the working branch to a particular commit.
While the built in diff viewer is a bit basic, it supports using Meld (see below) as an external diff viewer.
Tip: run gitk in your Git working directory to launch Gitk.
Gitk and Git-GUI are integrated, so once you’ve run one of the applications, you can launch the other from the menu bar.
Meld
Website: http://meldmerge.org
A GUI diff/merge tool with Git support.
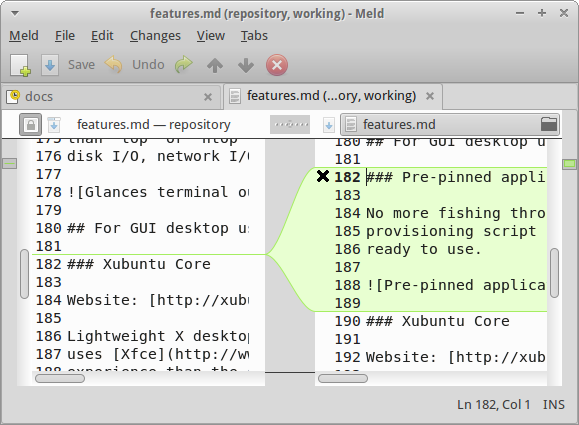
Tip: run meld . in your Git working directory to review your uncommitted
changes.
Git Credential Manager
Website: https://github.com/GitCredentialManager/git-credential-manager
Stores credentials for Git version control securely. Useful if you want to write to a Git repository using HTTPS rather than SSH.
GitHub CLI
Website: https://cli.github.com
GitHub CLI is a command line tool that makes it easy to interact with GitHub from the command line.
e.g. Cloning a GitHub repository
gh repo clone Netflix/flamescope
# Equivalent to:
# git clone git@github.com:Netflix/flamescope.git
e.g. Creating a pull request
gh pr create --title 'Pull request title here' --body 'Pull request body here.'
e.g. List issues for current repository
gh issue list
Git Interactive Rebase Tool
Website: https://github.com/MitMaro/git-interactive-rebase-tool
A terminal based sequence editor for Git rebase.
Postman
Website: https://www.getpostman.com
A user friendly tool for testing REST services.
For containerized development
Docker
Website: https://www.docker.com
Solves the problem of handling dependencies and common configuration between development, build, test and production.
When using a Docker image, there’s no more worrying if you have the correct
Java/Ruby/Python version installed, or is the JAVA_HOME set to the correct
installation; all of that is provided in the Docker image, you just use it.
It’s also easy to build your own Docker images so you can get the same benefits with your own software.
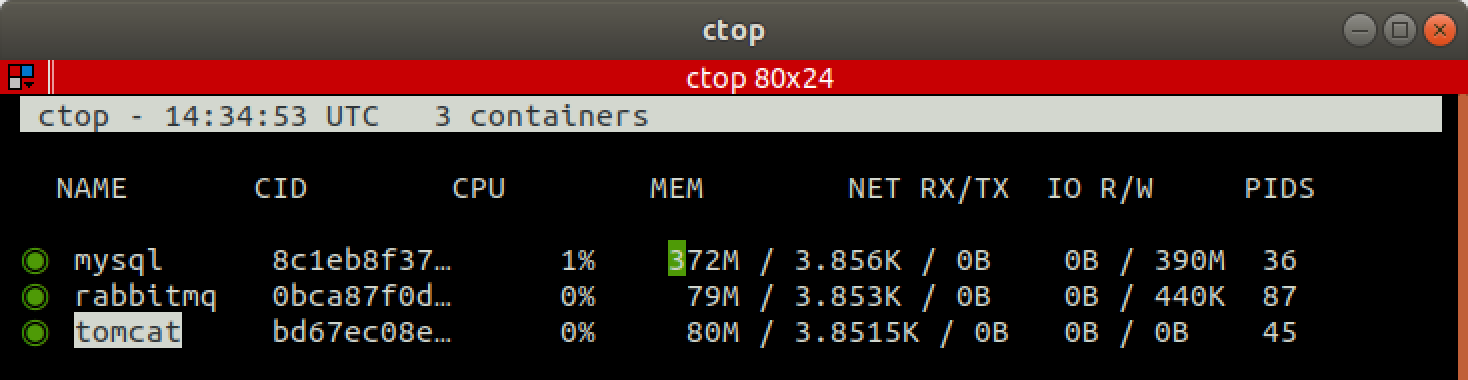
ctop
Website: https://ctop.sh
ctop is the terminal based tool that provides a top like interface for
container metrics. View CPU, memory, network I/O, and disk I/O for your
Docker containers at a glance from your terminal.
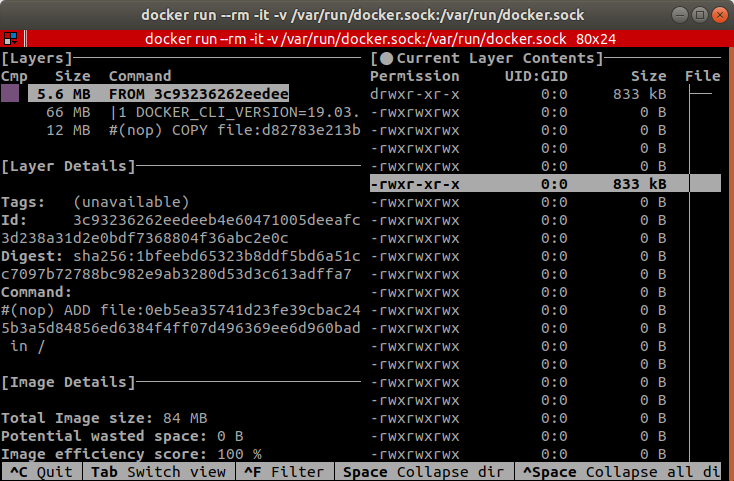
dive
Website: https://github.com/wagoodman/dive
dive is a tool for exploring docker images, layer contents, and discovering
ways to shrink Docker images.
Kubernetes
Website: http://kubernetes.io
Kubernetes is the leading solution for managing containerized applications in production.
Docker is great for running containerized applications locally, but you need something more to manage containerized applications across multiple servers. There’s Docker Swarm and Apache Mesos but the most popular solution is Kubernetes.
Kubernetes allows you to deploy services to a cluster of servers, to manage configuration, configure networking, perform rolling updates and much more.
Minikube
Website: https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube
Minikube makes it easy to run a single node Kubernetes cluster in the development environment.
Give it a try by running the following from the terminal:
minikube start
minikube dashboard
Note: because we’re already running inside a VM we’re running Minikube with
--vm-driver=none using a Zsh
plugin.
Helm
Website: https://helm.sh
Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes. It makes it easier to use software built for Kubernetes.
Give it a try by running the following from the terminal:
# Start Minikube (if you haven't already)
minikube start
# Initialize helm (if you haven't already)
helm init
# Wait for tiller to be ready
# You can watch the tiller status be ready (1/1) by running:
kubectl get pods -w --namespace kube-system
# terminate with ctrl-c
# Install Apache Tomcat
helm install stable/tomcat
# helm will give the service a name <something>-tomcat
# you can access the tomcat by running:
http "$(minikube service --url <something>-tomcat)"
# You'll get a HTTP 404 response (we haven't provided a
# webarchive), but you'll see it's come from a
# `Apache-Coyote` server.
Kompose
Website: http://kompose.io
Kompose is a conversion tool to go from Docker Compose to Kubernetes.
Give it a try by running the following from the terminal:
# Start Minikube (if you haven't already)
minikube start
# cd into a docker-compose project
# or use wget to download the following example compose file
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/kompose/master/examples/docker-compose-v3.yaml \
-O docker-compose.yaml
# Bring up your services
kompose up
# Watch your services load
kubectl get pods -w
# terminate with ctrl-c
# Once you're done shutdown the services
kompose down
# Once you're done with the Minikube instance
minikube stop
minikube delete
For Java developers
Open JDK
To get free patches for longer this project uses builds from AdoptOpenJDK.
Maven
Maven 3.9.4 is installed by default.
Note: Gradle is not installed as Gradle users are recommended to use the Gradle Wrapper.
IntelliJ IDEA plugins
- Maven Helper
adds the Dependency Analyzer tab to the editor panel for
pom.xmlfiles. - CheckStyle-IDEA for checking the code style of your Java source files.
- Concise AssertJ Optimizing Nitpicker to help you write more concise assertions using AssertJ.
- Log Support 2 code inspections for Slf4j.
IntelliJ code style
GantSign Code Style has support for the following JVM languages:
- Java: based on the Google Java Style Guide
- Kotlin: based on the Kotlin Style Guide
IntelliJ inspection profile
The GantSign Inspection Profile has support for Java and Kotlin. This is a strict inspection profile intended for greenfield code.
SDKMAN!
Website: https://sdkman.io
SDKMAN! is a tool for managing parallel versions of multiple Software Development Kits. It’s similar to RVM but for Java, Groovy, Kotlin, Scala, Maven, Gradle and a bunch of other JVM based SDKs.
To switch Java version in the current shell:
sdk use java 11
To change the default Java version:
sdk default java 11
To install Gradle:
sdk install gradle
To play with GraalVM:
# List available versions
sdk list java
# Install latest GraalVM version
sdk install java 17.0.8-graalce
# Switch to GraalVM in the current shell
sdk use java 17.0.8-graalce
To list all the supported SDKs:
sdk list
For Node.js developers
Node.js runtime
This development environment comes with Node.js v18 installed.
Pre-installed global packages
To provide a better out of the box experience the following global packages come pre-installed.
- Grunt task runner
- Gulp task runner
- npm-check-updates dependency version upgrade tool
- TS Node CLI TypeScript support
- Typings TypeScript definition manager
IDE support
Visual Studio Code comes with excellent support for Node.js, JavaScript and TypeScript.
IntelliJ code style
GantSign Code Style has support for JavaScript based on JavaScript Standard Style.
For Python developers
Pyenv version manager
Website: https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv
Pyenv lets you install and switch between multiple versions of Python. Other tools such as Pipenv use Pyenv when they need a version of Python you don’t currently have installed.
Pipenv package manager
Website: https://pipenv.readthedocs.io
Pipenv helps you manage a virtualenv for your projects as well as managing
your packages. It will add/remove packages from your Pipfile as you
install/uninstall packages. It also generates the Pipfile.lock for
deterministic builds.
Python plugin for Visual Studio Code
This development environment comes with Microsoft’s excellent Python plugin for Visual Studio Code: ms-python.python.
Tip: launch Visual Studio Code from your Pipenv shell. This will give Visual
Studio Code access to your virtualenv and let it install packages e.g. pylint,
autopep8 and rope without needing sudo.
To launch Visual Studio Code from your Pipenv shell run the following commands:
cd your-python-project
pipenv shell
code .
Python plugin for IntelliJ IDEA
Depending whether you’re using the IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition or the Ultimate Edition a different plugin will be installed. If you’re using IntelliJ IDEA Community Edition the plugin installed will provide equivalent functionality to PyCharm Community Edition. If you’re using IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate Edition the plugin installed will provide equivalent functionality to PyCharm Professional Edition.
Tip: launch IntelliJ from your Pipenv shell. This will give IntelliJ access
to your virtualenv and let it install packages e.g. pylint, autopep8 and
rope without needing sudo.
To launch IntelliJ from your Pipenv shell run the following commands:
cd your-python-project
pipenv shell
idea .
For Ansible developers
Molecule Wrapper Zsh support
Website: https://github.com/gantsign/molecule-wrapper
Molecule is an excellent tool to assist you in developing and testing Ansible Roles and Playbooks.
Molecule integrates with Docker to provide an isolated environment to try your provisioning and uses Testinfa to test the results.
Molecule can be tricky to install and that’s where Molecule Wrapper comes in. Molecule Wrapper is a shell script that installs Molecule (and its dependencies) before invoking Molecule.
The Zsh support for Molecule Wrapper adds an alias so you can run ./moleculew
with the molecule command and enables tab-completion support.